Night vision thermal imaging technology has revolutionized the way we perceive our surroundings in low-light conditions. This advanced technology allows users to detect heat emitted by objects, making it invaluable for various applications, from military operations to wildlife observation.

What is Night Vision Thermal Imaging?
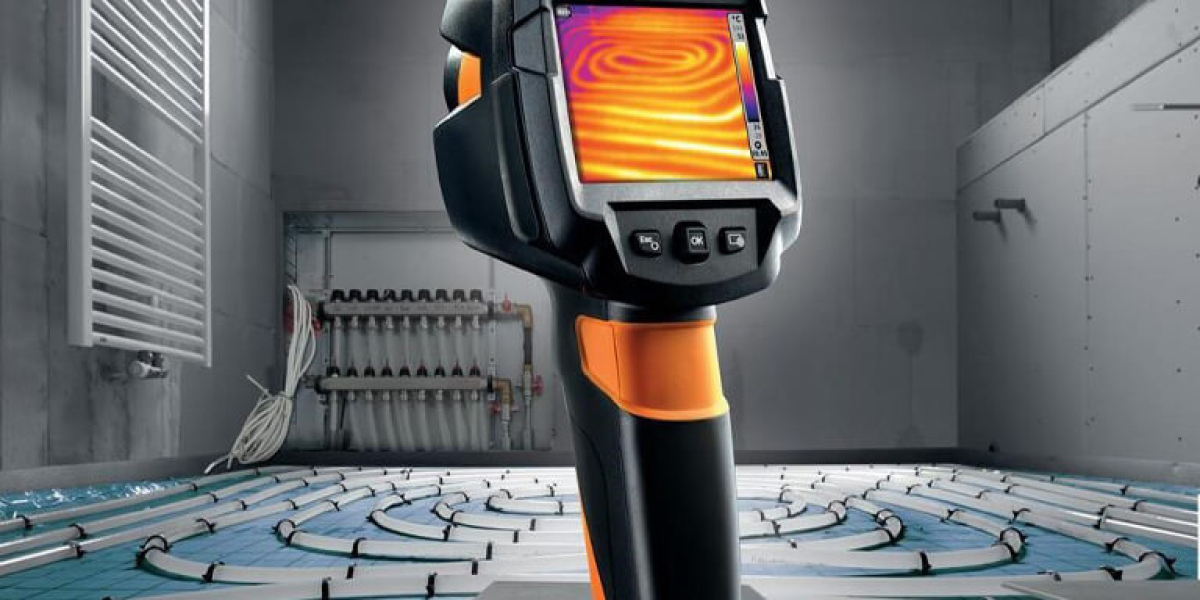
Night vision thermal imaging refers to the process of capturing infrared radiation emitted by objects and converting it into a visible image. Unlike traditional night vision devices that amplify existing light, thermal imaging detects heat signatures, enabling users to see in complete darkness. This capability is particularly useful in scenarios where visibility is compromised.
How Does Night Vision Thermal Work?
The core principle behind night vision thermal imaging lies in the detection of infrared radiation. All objects emit thermal energy, which is then captured by a thermal sensor. The sensor converts this energy into an electronic signal, which is processed to create a thermal image. The resulting image displays varying temperatures in different colors, allowing users to identify warm objects against cooler backgrounds.
- Detection: Thermal sensors detect infrared radiation emitted by objects.
- Conversion: The detected energy is converted into an electronic signal.
- Image Creation: The electronic signal is processed to produce a thermal image.
Applications of Night Vision Thermal Imaging
Night vision thermal technology has a wide range of applications across various fields. Here are some notable uses:
- Military and Law Enforcement: Thermal imaging is crucial for surveillance, target acquisition, and reconnaissance missions.
- Search and Rescue Operations: It aids in locating missing persons or victims in low-visibility conditions.
- Wildlife Observation: Enthusiasts use thermal imaging to monitor animal behavior without disturbing their natural habitat.
- Building Inspections: Professionals utilize thermal cameras to identify heat loss, moisture intrusion, and electrical issues.
Choosing the Right Night Vision Thermal Device
When selecting a night vision thermal device, consider the following factors:
- Resolution: Higher resolution provides clearer images.
- Detection Range: Assess how far you need to detect heat signatures.
- Battery Life: Longer battery life ensures extended use in the field.
For more detailed guidance on using thermal scopes during the day, visit this comprehensive guide.
Conclusion
In summary, night vision thermal imaging is a powerful tool that enhances visibility in darkness by detecting heat signatures. Its diverse applications make it an essential technology for professionals and enthusiasts alike. Understanding how this technology works and its various uses can help you make informed decisions when selecting the right thermal imaging device for your needs.